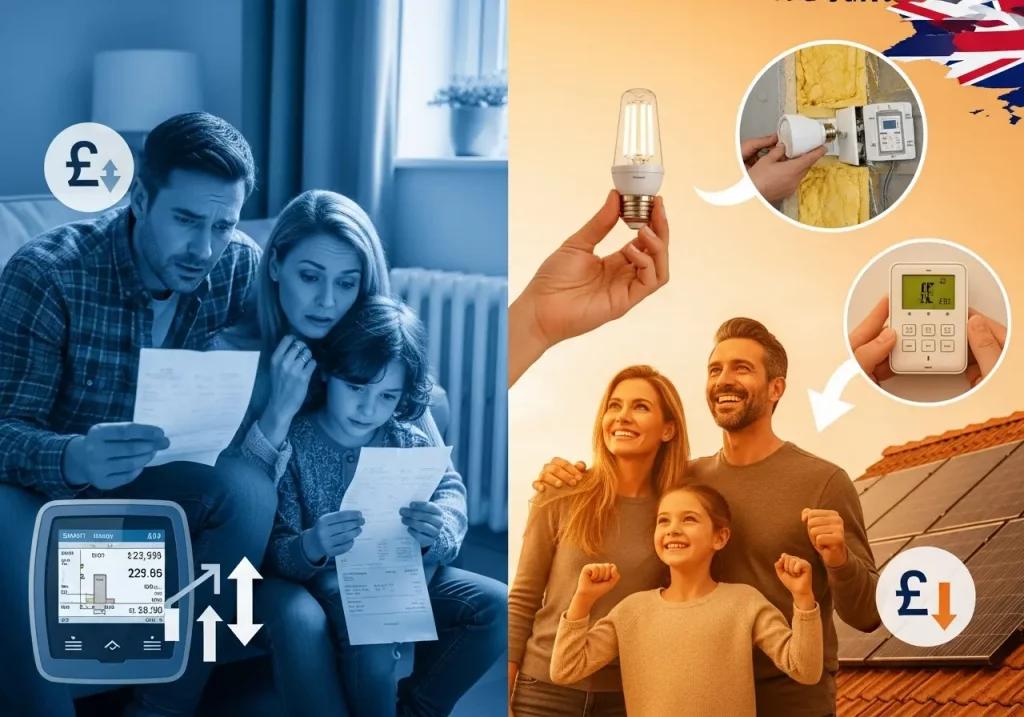
Are Energy Bills Going Up or Down in 2025?
If you’re a UK household struggling with energy costs, you’re not alone. Despite recent decreases from the peak of the energy crisis in 2022-2023, energy bills remain significantly higher than pre-crisis levels, leaving millions of families searching for answers and solutions.
The energy price cap has been on a rollercoaster journey throughout 2024-2025, and understanding where it’s heading in 2026 is crucial for household budgeting. This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about UK energy bills, the price cap changes, government support, and practical ways to reduce your costs.
Understanding the Current Energy Price Cap (January 2025 – April 2025)
What Is the Energy Price Cap?
The energy price cap is set by Ofgem, the UK’s energy regulator, and limits how much energy suppliers can charge customers per unit of gas and electricity. It’s updated quarterly and applies to approximately 29 million households on standard variable tariffs.
The price cap doesn’t limit your total bill—it caps the unit rates and standing charges. If you use more energy, you’ll pay more; if you use less, you’ll pay less.
Current Price Cap Levels
January to March 2025: The price cap stands at £1,738 per year for a typical dual-fuel household paying by direct debit—a modest 1% rise of £21 from the previous quarter.
April to June 2025: Forecasts suggest the cap could decrease by approximately 2% to around £1,700 per year, though this remains subject to wholesale market conditions.
While these figures might seem reasonable, they’re still 44% higher than winter 2021/22 levels, before the energy crisis began. This means UK households are paying substantially more for energy than they were just three years ago.
Why Are Energy Bills Still So High?
Several interconnected factors keep energy prices elevated:
1. Global Energy Markets
The Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 dramatically disrupted global gas supplies, causing wholesale prices to spike. While prices have decreased from their 2022 peaks, they remain elevated compared to pre-crisis levels.
2. Wholesale Price Volatility
Wholesale gas and electricity prices remain volatile due to:
- Ongoing geopolitical tensions
- Global demand fluctuations
- Weather patterns affecting renewable generation
- Supply chain constraints
3. Infrastructure and Network Costs
Energy suppliers face increasing costs for:
- Maintaining and upgrading the UK’s aging energy infrastructure
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources
- Network improvements and grid modernization
- Standing charges that cover these fixed costs
4. Policy and Taxation Changes
The UK government’s October 2024 Autumn Budget introduced significant changes to energy taxation:
- The Energy Profits Levy (windfall tax) on oil and gas companies increased from 35% to 38%
- The 29% investment allowance for these companies was removed
- Total tax rate on oil and gas activities now stands at 78%
While these measures aim to fund green energy initiatives, they may influence long-term energy investment and pricing.
Energy Price Forecasts: What to Expect in 2025
Energy analysts predict continued uncertainty throughout 2025:
Short-Term Outlook (Early 2025)
Expert forecasts suggest the price cap could decrease by approximately 2% in April 2025, potentially dropping to around £1,700 per year. However, these predictions remain uncertain and could change based on:
- Winter weather severity
- Global energy market developments
- Geopolitical events
- Supply and demand fluctuations
Medium-Term Outlook (Mid to Late 2025)
There’s little prospect of energy bills returning to pre-crisis levels in the foreseeable future. Most experts agree that:
- Bills will remain substantially above 2021 levels
- Seasonal variations will continue (higher in winter, lower in summer)
- Gradual price stabilization is more likely than dramatic decreases
- Renewable energy transition may eventually stabilize costs
How the UK Energy Crisis Unfolded: A Timeline
Understanding how we reached this point helps contextualize current prices:
2021: The Beginning
- Summer 2021: Global energy prices began rising as economies reopened post-pandemic
- Increased demand met constrained supply, causing wholesale price increases
2022: Crisis Peak
- February 2022: Russia invaded Ukraine, triggering massive price spikes
- April 2022: Price cap increased by 54%
- October 2022: Government introduced Energy Price Guarantee (EPG) at £2,500 to prevent a planned 80% price cap increase
- Annual bills rose 27% despite the EPG protection
2023: Stabilization Begins
- January-June 2023: EPG maintained at £2,500
- July 2023: EPG ended as price cap fell to £2,074
- October 2023: Price cap dropped to £1,923
2024: Modest Fluctuations
- January 2024: Slight increase to £1,928
- April 2024: Decrease to £1,690
- July 2024: Further decrease to £1,568
- October 2024: Increase to £1,717
2025: Uncertain Future
- January 2025: Small increase to £1,738 confirmed
- Future quarters remain unpredictable
UK Fuel Poverty: The Hidden Crisis
The sustained high energy costs have created a fuel poverty crisis affecting millions of UK households.
What Is Fuel Poverty?
A household is considered to be in fuel poverty when it needs to spend more than 10% of its income (after housing costs) on domestic energy to maintain an adequate level of warmth and meet other energy needs.
Current Statistics
- 6.1 million UK households are estimated to be in fuel poverty as of January 2025
- This represents approximately 20% of all UK households
- The number peaked at 8.4 million households during the height of the crisis
- Even with price decreases, 2.3 million households are paying more than at the crisis peak due to increased usage and changed circumstances
Who Is Most Affected?
Fuel poverty disproportionately impacts:
- Pensioners and elderly households
- Low-income families
- People with disabilities
- Those in poorly insulated homes
- Rural communities dependent on heating oil
- Prepayment meter customers (though the premium has been eliminated)
Government Support and Schemes Available
Current Support Measures (2024-2025)
1. Warm Home Discount
- £150-£200 annual payment to eligible low-income households
- Eligibility expanded in 2025 to include almost 3 million more households
- Applied automatically to your electricity bill between October and March
2. Winter Fuel Payment (Means-Tested)
- Now means-tested rather than universal
- Available to pensioners receiving certain benefits
- £200-£300 depending on circumstances
3. Cold Weather Payments
- £25 for each 7-day period of very cold weather (below 0°C average)
- Automatic payments to eligible households on certain benefits
4. Energy Company Obligation (ECO4)
- Free or subsidized home energy efficiency improvements
- Available to low-income and vulnerable households
- Includes insulation, boiler upgrades, and renewable technologies
5. Boiler Upgrade Scheme
- £5,000-£7,500 grants for heat pump installations
- Aims to encourage transition to low-carbon heating
- Increased funding announced in 2024 Autumn Budget
The Warm Homes Plan
The government’s new Warm Homes Plan represents a significant long-term investment:
- £3.4 billion allocated over the next three years (first installment of £13.2 billion total commitment)
- £1.8 billion dedicated to fuel poverty schemes
- Expected to help over 225,000 low-income households
- Aim to reduce annual energy bills by £200+ through energy efficiency improvements
Practical Ways to Reduce Your Energy Bills
While you can’t control the price cap, you can control your usage and home efficiency. Here are evidence-based strategies to lower your costs:
Immediate Actions (Zero or Low Cost)
1. Switch to the Best Tariff
- Compare your current tariff with alternatives using comparison websites
- Consider fixing if fixed-rate deals are cheaper than the price cap
- Check for exclusive deals with your current supplier
2. Apply for Available Support
- Check eligibility for Warm Home Discount, Winter Fuel Payment, and Cold Weather Payments
- Contact your local council about additional local support schemes
- Speak with your energy supplier about hardship funds if struggling
3. Reduce Energy Waste
- Turn off lights when leaving rooms
- Unplug devices and chargers when not in use (standby power costs £35-£80 annually)
- Use lids on pans when cooking
- Only boil the water you need in kettles
- Wash clothes at 30°C instead of 40°C
- Air-dry laundry when possible instead of using tumble dryers
4. Optimize Heating
- Lower your thermostat by just 1°C (saves approximately £80-£100 per year)
- Use a timer to heat your home only when needed
- Close curtains at dusk to retain heat
- Bleed radiators to improve efficiency
- Keep furniture away from radiators
5. Take Shorter Showers
- Reducing shower time from 10 to 4 minutes saves around £95 per year
- Consider installing a water-efficient showerhead
Medium-Term Investments (£100-£1,000)
1. LED Lighting
- Replace all bulbs with LED equivalents
- LEDs use 90% less energy than traditional bulbs
- Typical savings: £35-£65 per year
- Bulbs last 15-25 years
2. Smart Thermostats
- Cost: £150-£300 installed
- Provides precise temperature control and scheduling
- Typical savings: £75-£150 per year
- Many energy suppliers offer free or discounted smart thermostats
3. Draught-Proofing
- Seal gaps around windows, doors, and letterboxes
- DIY cost: £50-£150
- Professional installation: £200-£400
- Typical savings: £45-£85 per year
4. Hot Water Tank Insulation
- Install a hot water tank jacket
- Cost: £15-£30
- Typical savings: £35-£70 per year
- Payback period: Less than 6 months
5. Reflective Radiator Panels
- Place heat-reflective panels behind radiators on external walls
- Cost: £10-£15 per radiator
- Reflects heat back into the room instead of warming the wall
Long-Term Investments (£1,000+)
1. Loft Insulation
- One of the most cost-effective improvements
- Cost: £300-£900 for DIY, £500-£1,500 professionally installed
- Typical savings: £355+ per year
- May be free or subsidized under ECO4 scheme
- Payback period: 2-4 years
2. Cavity Wall Insulation
- Cost: £500-£1,500
- Typical savings: £380+ per year
- Often available free or subsidized under ECO4
- Payback period: 2-4 years
3. Double or Triple Glazing
- Cost: £4,000-£13,000 for a typical home
- Typical savings: £145-£180 per year
- Additional benefits: Noise reduction, increased property value
- Longer payback period: 20-40 years
4. Modern Condensing Boiler
- Replace boilers over 15 years old
- Cost: £2,000-£4,500 installed
- Typical savings: £305-£590 per year
- Payback period: 5-10 years
- May qualify for government grants
5. Heat Pump Installation
- Cost: £10,000-£18,000 (before grants)
- Boiler Upgrade Scheme provides £5,000-£7,500 grant
- Typical running cost savings: Variable, depends on current system
- Long-term benefits: Future-proof, low carbon
- Best suited for well-insulated homes
6. Solar Panels
- Cost: £5,000-£11,000 for a typical 4kW system
- Typical savings: £350-£600 per year on electricity bills
- Additional income through Smart Export Guarantee
- Payback period: 10-15 years
- Increases property value
Energy-Efficient Appliances
When replacing appliances, choose the most efficient models:
- Fridges and Freezers: Look for high energy ratings; an A-rated model uses 40% less energy than older models
- Washing Machines: Choose A-rated models with eco settings
- Dishwashers: A-rated models with eco mode save money and water
- Ovens: Fan-assisted and induction hobs are most efficient
- TVs: LED/OLED TVs use less power than older LCD and plasma models
Understanding Your Energy Bill
Breaking down your energy bill helps identify where costs come from and how to reduce them.
Unit Rates (Per kWh)
This is what you pay for each unit of energy used:
- Electricity: Approximately 24.5p per kWh
- Gas: Approximately 6.0p per kWh
Your actual usage determines most of your bill cost. Typical annual usage:
- Electricity: 2,700 kWh for an average household
- Gas: 11,500 kWh for an average household
Standing Charges
Fixed daily charges covering:
- Maintaining the energy network
- Meter readings and maintenance
- Supplier administration costs
Current typical standing charges:
- Electricity: 53-60p per day (£193-£219 per year)
- Gas: 29-31p per day (£106-£113 per year)
Payment Methods
Your payment method affects costs:
Direct Debit (Cheapest)
- Monthly fixed payments based on estimated annual usage
- Smooths costs across the year
- Usually the best available rate
Prepayment Meter
- Pay before you use
- Historically more expensive, but the premium was abolished in 2023
- Good for budgeting but requires regular top-ups
Payment on Receipt of Bill (Most Expensive)
- Pay quarterly after receiving bill
- Typically £50-£100 more expensive annually than direct debit
Smart Meters: Should You Get One?
Smart meters are digital energy meters that automatically send readings to your supplier, eliminating estimated bills.
Benefits
- Accurate billing: No more estimated readings
- Real-time monitoring: In-home display shows current energy use
- Easier switching: Automatic meter readings speed up supplier switches
- Time-of-use tariffs: Access to tariffs with cheaper off-peak rates
- Better budgeting: See exactly what you’re spending
Considerations
- First-generation (SMETS1) meters may lose smart functionality when switching suppliers
- Second-generation (SMETS2) meters maintain functionality across suppliers
- Installation is free
- You have the right to refuse installation
- Smart meters don’t reduce energy bills themselves—only behavior change saves money
The Future: Green Energy and Great British Energy
The UK government’s commitment to becoming a “clean energy superpower” will shape future energy costs and supply.
Great British Energy
Launched in July 2024, Great British Energy is a new publicly owned energy company with:
- £8.3 billion initial capitalization
- £125 million funding for 2025-2026
- Mission to drive clean energy investment and lower bills
- Headquarters in Aberdeen, Scotland
National Wealth Fund
Supporting clean energy transition with:
- Initial capitalization aimed at catalyzing £70 billion in private investment
- Focus on renewable energy infrastructure
- Support for green industries and jobs
Long-Term Implications
The transition to renewable energy could:
- Stabilize prices: Reduce dependence on volatile global fossil fuel markets
- Lower costs: Renewable generation costs continue falling
- Increase energy security: Domestic production reduces import dependence
- Create jobs: Investment in green technology and infrastructure
- Achieve climate goals: Decarbonize electricity grid by 2030
However, short-term costs of this transition may keep prices elevated as infrastructure is built and upgraded.
Energy Bills and Climate Change: The Bigger Picture
The UK’s energy transition isn’t just about costs—it’s crucial for meeting climate targets.
UK Climate Commitments
- Net Zero by 2050: Legal obligation to eliminate net greenhouse gas emissions
- 78% reduction by 2035: Interim target for emissions reduction from 1990 levels
- Decarbonized power grid by 2030: Ambitious target requiring massive renewable energy expansion
Your Role
Every household’s energy choices contribute to national emissions:
- Home heating accounts for approximately 14% of UK emissions
- Energy efficiency improvements reduce both costs and carbon footprint
- Renewable energy adoption accelerates the transition
- Reduced consumption has immediate climate benefits
By improving your home’s energy efficiency, you simultaneously save money and help combat climate change.
Common Energy Bill Myths Debunked
Myth 1: “Leaving Heating on Low All Day Is Cheaper”
False: It’s more efficient to heat your home only when needed using a timer. Leaving heating on low all day means heat is constantly escaping, requiring continuous energy input.
Myth 2: “Energy-Saving Measures Are Too Expensive to Be Worth It”
False: Many measures have payback periods of less than 5 years, and some (like LED bulbs and draught-proofing) pay for themselves within months. Government grants can reduce or eliminate upfront costs for major improvements.
Myth 3: “Fixed-Rate Tariffs Are Always Better”
Not Always: Fixed rates made sense when prices were stable or rising, but they can be more expensive than the price cap when wholesale prices fall. Always compare before fixing.
Myth 4: “Switching Energy Suppliers Is Complicated and Risky”
False: The switching process is straightforward, typically takes 3 weeks, and is protected by regulation. You won’t experience any service interruption.
Myth 5: “Smart Meters Automatically Save You Money”
False: Smart meters provide information, but savings only come from changing your behavior based on that information. They’re a tool, not a solution in themselves.
Myth 6: “Renewable Energy Is Always More Expensive”
False: Renewable electricity is now among the cheapest forms of new power generation globally. The UK’s energy costs remain high due to gas dependency and infrastructure costs, not renewable energy.
Regional Differences in UK Energy Costs
Energy costs vary across the UK due to different distribution networks and regional factors.
Highest Cost Areas
- Scotland (particularly Highlands and Islands): Remote location increases distribution costs
- Southern England: High standing charges due to network investment
- Wales (rural areas): Distribution costs for dispersed populations
Lowest Cost Areas
- Yorkshire: Historically lower distribution costs
- East Midlands: Competitive network charges
- North West England: Economies of scale in urban areas
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland has a separate energy market and regulatory system:
- Different pricing structures
- Historically different subsidy schemes
- Currently, prices are higher than in Great Britain
Special Circumstances and Vulnerable Customers
Priority Services Register
Energy suppliers must maintain a Priority Services Register for customers who:
- Are pensioners
- Have disabilities
- Have chronic illnesses
- Have mental health conditions
- Are visually or hearing impaired
- Have young children
Benefits of Registration
- Advance notice of supply interruptions
- Priority reconnection after power cuts
- Free annual gas safety checks for some suppliers
- Password protection for doorstep visits
- Bills in alternative formats (large print, Braille, audio)
- Extra support during cold weather
Prepayment Meter Protections
If you have a prepayment meter:
- Emergency credit available during supply hours
- Friendly credit on weekends and bank holidays
- Suppliers must offer advice on debt management
- New rules prevent forced prepayment meter installations in vulnerable households
Can’t Pay Your Energy Bill?
If you’re struggling with energy debt:
- Contact your supplier immediately: They must help you create an affordable payment plan
- Access hardship funds: Many suppliers have dedicated funds for customers in financial difficulty
- Seek debt advice: Organizations like Citizens Advice and StepChange offer free, confidential support
- Check benefit entitlement: You may be eligible for additional financial support
- Never ration energy dangerously: Your health and safety come first
Taking Action Today
The combination of high energy costs and the ongoing cost-of-living crisis makes energy bill management more critical than ever for UK households.
Your Action Plan
Week 1: Assessment
- Review your current energy bills and tariff
- Check your actual vs. estimated usage
- Identify your biggest energy-consuming activities
- Research available government support schemes
Week 2: Quick Wins
- Apply for any support schemes you’re eligible for
- Switch to LED bulbs
- Implement zero-cost energy-saving habits
- Check if your current tariff is competitive
Month 1: Medium-Term Improvements
- Consider smart thermostat installation
- Complete draught-proofing
- Insulate hot water tank
- Sign up for Priority Services Register if eligible
Months 2-6: Major Improvements
- Apply for ECO4 scheme if eligible
- Get quotes for loft and cavity wall insulation
- Investigate renewable energy options
- Plan for any boiler replacement needs
Long-Term: Future-Proofing
- Monitor energy market developments
- Stay informed about new government schemes
- Consider heat pump installation when replacing your boiler
- Evaluate solar panel investment
Conclusion: Navigating the New Energy Landscape
UK energy bills in 2024-2025 remain significantly higher than pre-crisis levels, with little prospect of returning to those prices in the foreseeable future. The energy price cap provides some protection, but at £1,738 per year (January 2025), typical households are paying 44% more than in winter 2021/22.
However, this challenge also presents an opportunity. The combination of government support schemes, technological improvements, and your own energy-saving actions can substantially reduce your costs while contributing to the UK’s climate goals.
Whether you’re implementing simple behavior changes, investing in home improvements, or accessing government support schemes, every action counts. In an era of elevated energy costs, taking control of your energy use isn’t just good for your wallet—it’s essential for household budgeting and the planet’s future.
The path forward requires both individual action and systemic change. By making smart energy choices today, you’ll not only reduce your current bills but also prepare your home for a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: When will energy bills go back to normal? A: Unfortunately, experts don’t expect energy bills to return to pre-crisis levels in the near future. The “new normal” is likely to be significantly higher than 2021 levels, though prices should gradually stabilize.
Q: Should I fix my energy tariff or stay on the price cap? A: Compare available fixed rates with the current price cap. Only fix if the rate is cheaper than the cap and you’re comfortable locking in that price. Consider market forecasts and your risk tolerance.
Q: Can I get help if I can’t afford my energy bills? A: Yes. Contact your energy supplier immediately to discuss payment plans, access hardship funds, and explore government support schemes like the Warm Home Discount and ECO4.
Q: Are smart meters worth getting? A: Smart meters provide useful information about your energy use and ensure accurate billing, but they don’t automatically save money. They’re worth it if you’ll use the information to change your behavior.
Q: What’s the single most effective thing I can do to reduce my energy bills? A: Improving your home’s insulation (loft and cavity walls) typically provides the biggest return on investment, often available free or subsidized through the ECO4 scheme. For immediate impact, reducing your thermostat by 1°C saves around £80-£100 annually.